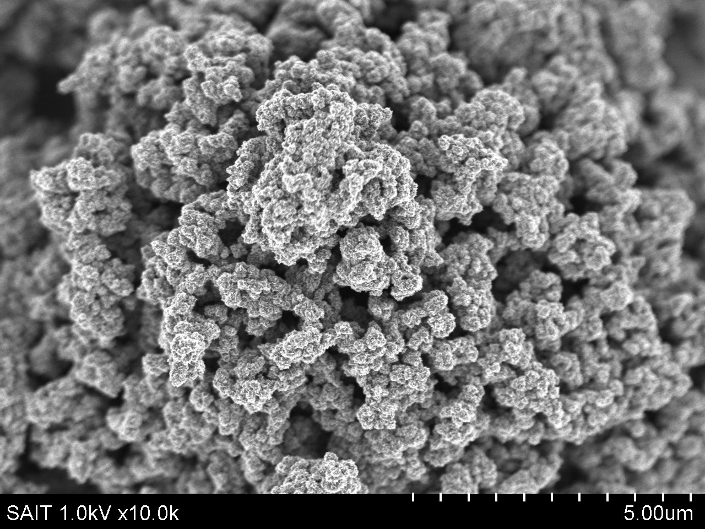
Samsung, the electronics giant, has developed a new graphene battery technology capable of charging five times faster than standard lithium-ion batteries, according to a Samsung press release posted Tuesday.
Researchers at the Samsung Advanced Institute of Technology (SAIT) have created something called a “graphene ball,” that increases lithiumi-ion battery charging speeds and adds 45% of increased capacity. Samsung says that SAIT worked with Samsung SDI and South Korea’s Seoul National University’s School of Chemical and Biological Engineering to make the breakthrough.
How fast is that? Samsung says graphene ball batteries would only require 12 minutes to fully charge while maintaining “stable battery temperatures” that could be useful not only for mobile devices, but electric vehicles as well.
In order to create this technology, SAIT molded and synthesized graphene, known for its conductivity and strength, into a popcorn-like shape using silica. They used this for the anode and cathode materials within lithium-ion batteries.
From the release:
Dr. Son In-hyuk, who led the project on behalf of SAIT, said, “Our research enables mass synthesis of multifunctional composite material graphene at an affordable price. At the same time, we were able to considerably enhance the capabilities of lithium-ion batteries in an environment where the markets for mobile devices and electric vehicles is growing rapidly. Our commitment is to continuously explore and develop secondary battery technology in light of these trends.”
The science journal Nature also wrote about the research in this month’s issue, breaking down all of the technical scientific details of the research.
From the abstract:
“The graphene-ball coating improves cycle life and fast charging capability by suppressing detrimental side reactions and providing efficient conductive pathways. The graphene ball itself also serves as an anode material with a high specific capacity of 716.2 mAh g−1. A full-cell incorporating graphene balls increases the volumetric energy density by 27.6% compared to a control cell without graphene balls, showing the possibility of achieving 800 Wh L−1 in a commercial cell setting, along with a high cyclability of 78.6% capacity retention after 500 cycles at 5C and 60 °C.”
Since the breakthrough of this research, SAIT has filed two patent applications for the “graphene ball” technology in the US and Korea, which suggests Samsung could develop products using this technology in the near future.
Source: Samsung
Samsung’s photograph caption above: *Graphene is a single layer of carbon atoms from graphite, and is receiving much attention in the battery and display industry due to its physical, chemical stability. Graphene is 100 times more effective than copper in conducting electricity and displays remarkable electron mobility – 140 times faster than silicon – which makes it an ideal material for fast charge.